
Therefore, megahertz WPT systems are discussed in this paper. Higher-frequency WPT technologies, i.e., gigahertz WPT technologies, are being developed for use in nanoscale and ultra-low-power systems for biomedical applications, wireless sensors, and microwave detection, which require far less power than the mobile devices mentioned above. Furthermore, compared to kilohertz WPT systems, megahertz WPT systems will be more compact, which is advantageous when charging multiple devices simultaneously. It will be promising for consumer electronics to achieve longer transmission distances in WPT systems by increasing the system frequency to megahertz. To improve the user experience, medium-range wireless power transfer (WPT) and multiple device charging technologies have attracted considerable attention from both academia and industry.
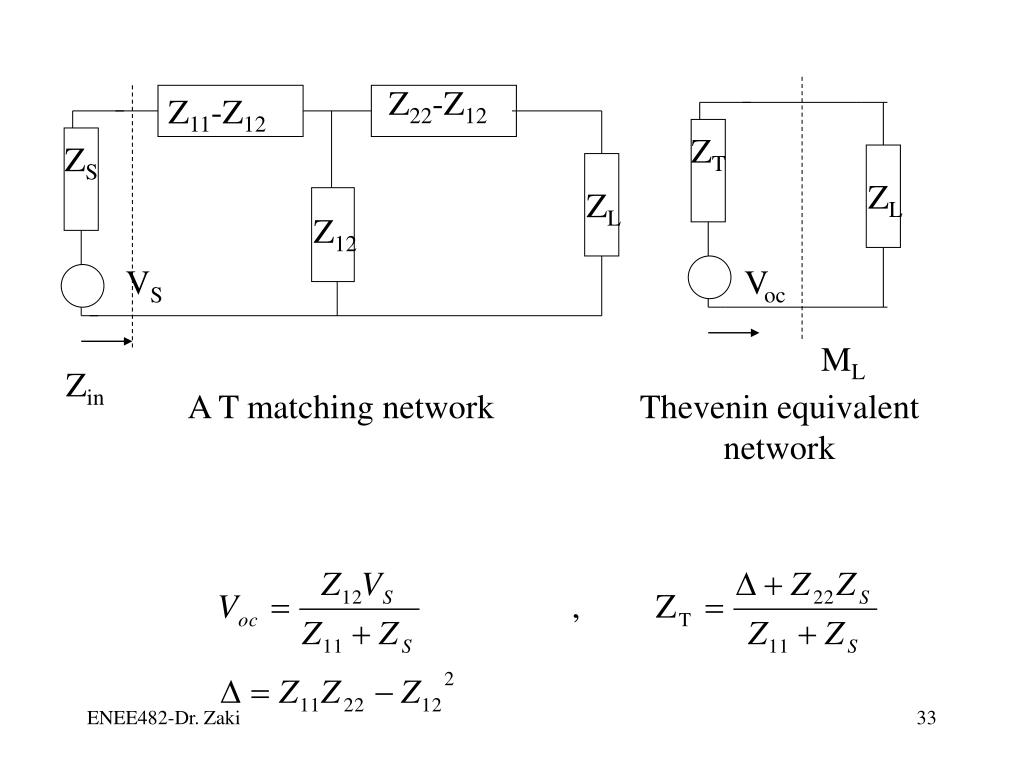
In recent years, inductive wireless power transfer systems have been widely used in mobile devices, such as cell-phones, smart watches, and earphones. The impedance matching method and design procedure in this paper could provide a practical solution for building a high-efficiency WPT system with strong robustness. The peak system efficiency reached 83.2% with 13.7 W output power. With a double-L-type IMN, the WPT system could maintain high efficiency (over 55%) under a wider range of coil coupling coefficient and load variations. The experimental results show that the proposed double-L-type IMN can significantly attenuate the decline in Class-E PA efficiency when system parameters dynamically change. A 6.78 MHz Class-E2-based WPT system was built to validate the proposed design method. Compared to a single L-type IMN, a double-L-type IMN is more flexible and has better tuning performance. The load-pull technique is adopted to identify the high-efficiency load region of a Class-E power amplifier (PA), and a double-L-type impedance matching network (IMN) is proposed to transform the load impedance of a Class-E PA into a high-efficiency working region. In this paper, an impedance matching method and a design procedure are proposed to maintain high system efficiency over a wider range of coupling coefficient and load variations. System efficiency decreases rapidly when the coil coupling coefficient and load deviate from their optimum values. I did a lot of the simulation in Excel.The performance of a conventional Class-E2-based WPT system is sensitive to system parameters such as the coil coupling coefficient and load variation. The calculations are simple enough I would just do it in Excel. And I have a suspicion that's the easy part, your power station impedance and the transmission line impedance is the hard part. I am just doing the impedance match thingy for you. And sorry I don't know anything about power station. The maximum power transfer is if the Z_s=Z_0, then you just terminate with the characteristic impedance of the transmission line and you are done, no worry about the distance or Smith Chart. If you can get through to this point, all you have to do is to terminate with complex conjugate and you get matching termination. Particular it is 3 phase and they do cross talk to each other. I am not particularly good in doing this. Also, Z_0\ is the characteristic impedance of the transmission line and you need to provide the dimension and structure of the power lines to determine. The difficult parameters are the Z_s which you have to find out. Since dielectric is air in power line, so \epsilon=\epsilon_0\ and speed of propagation is 3\times 10^8 m/sec\.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
